β-Galactosidase-cleavable linkers are a special class of chemically designed linker structures that can be cleaved under the action of a specific enzyme—β-galactosidase—thus triggering the precise release of drugs from the drug carrier. These linkers are widely applied in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), targeted drug delivery systems, and intelligent drug design. Leveraging strong ADC technology capabilities and extensive project experience, BOC Sciences is committed to providing global customers with high-quality custom development services for β-galactosidase-cleavable linkers. From initial design and synthetic process development to performance validation and regulatory support, we ensure the smooth implementation and successful translation of customer projects throughout the entire workflow.
Glycosidase-cleavable linkers are another commonly used enzyme category exploited in ADC development. These hydrolytic enzymes are typically confined to lysosomal compartments, but like cathepsin B, they can be secreted by tumor cells in necrotic areas. β-Glucuronidase and β-galactosidase cleavable linkers are the most used type of glycosidase-cleavable chemistry currently in use. Similar to β-glucuronidase, β-galactosidase is overexpressed in certain tumor types. Mechanistically, β-galactosidase is analogous to β-glucuronidase in its hydrolytic activity but instead hydrolyses β-galactoside. Researchers found that β-galactosidase-sensitive antibody-drug conjugates utilizing this type of linker, when used with trastuzumab and MMAE, were more potent than the Val-Cit-PABC analog. Furthermore, this linker-payload combination was more efficient than the previously approved drug trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) for treating HER2+ mammary tumors in mice.
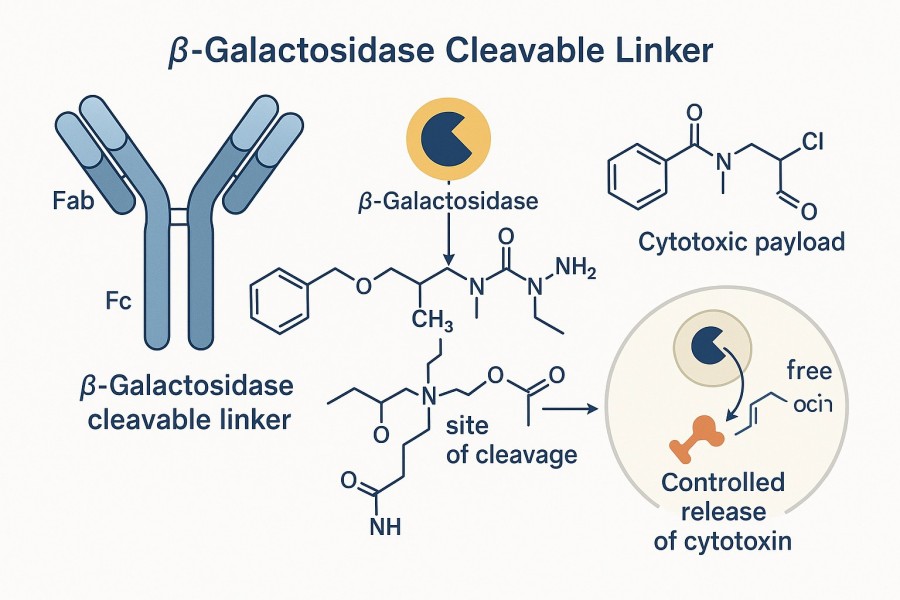 Fig. 1. β-galactosidase sensitive linker in antibody-drug conjugates (BOC Sciences Authorized).
Fig. 1. β-galactosidase sensitive linker in antibody-drug conjugates (BOC Sciences Authorized).
Recently, the use of β-galactosidase cleavable linkers for ADCs was reported incorporating a PEG10 spacer. In terms, the spacer was substituted by a nitro group in order to increase the rate of self-immolation. By the analogy of β-glucuronidase linkers, the cleavage mechanism involves the hydrolysis of the β-galactosidase moiety, which confers hydrophilicity to the chemical precursor. Another advantage is that the β-galactosidase enzyme is present only in the lysosome, whereas β-glucuronidase is expressed in lysosomes and also in the microenvironment of solid tumors.
As a global leading provider of life sciences and chemical synthesis services, BOC Sciences has deeply cultivated the ADC field for many years and possesses rich experience in linker design and synthesis. For β-galactosidase-cleavable linkers, we offer customers fully customized end-to-end development services to ensure that each project meets stringent scientific research and production requirements. Our service scope includes:
Based on client needs, BOC Sciences' expert team uses advanced computational chemistry simulations and enzyme-substrate binding models to design multiple linker structures with high enzyme sensitivity and stability. Key focuses during design include:
BOC Sciences boasts a comprehensive organic and carbohydrate chemistry synthesis platform, capable of producing high-purity β-galactosidase-sensitive linkers. Our services include:
To ensure the reliability of linkers in practical applications, BOC Sciences provides comprehensive functional validation services:
Upon project completion, we also offer process technology transfer support to assist customers in stable batch production on their own manufacturing lines. Additionally, BOC Sciences provides detailed technical documents and process reports, including:
Focusing on the two core components, payload and antibody, BOC Sciences provides precise, efficient, and highly compatible linker solutions. By optimizing linker structures, we achieve efficient enzymatic cleavage release of payloads while ensuring the functional integrity and conjugation stability of antibodies, empowering customers to develop targeted therapeutics with superior performance. Our professional team combines advanced synthetic techniques and enzymology principles to meet the personalized needs of diverse clients.
BOC Sciences' design of β-galactosidase cleavable linkers for the payload side emphasizes chemical compatibility, stability, and enzymatic release efficiency, ensuring precise payload release inside target cells.
Design Highlights:
As the targeting component of ADCs, antibodies have complex structures and sensitive functions. BOC Sciences' design of β-galactosidase-cleavable linkers for the antibody side focuses on efficient conjugation, stable binding, and preserving antibody functionality.
Design Highlights:
Years of accumulated antibody conjugation and linker R&D experience, successfully supporting multiple ADC projects, with rich hands-on expertise in solving complex structural design and process challenges.
Equipped with advanced synthesis and analytical instruments, focusing on innovative development of enzyme-sensitive linkers to ensure efficient design and precise performance validation.
Providing end-to-end customized services from structural design to scale-up production, flexibly responding to diverse R&D goals tailored to client-specific needs.
Implementing multi-level quality control covering raw materials, synthesis, and final product testing, guaranteeing high standards of stability and functionality for linker products.
Covering the entire industrial chain from design, synthesis, characterization to pilot scale-up and GMP-grade manufacturing, responding swiftly to project progress and facilitating efficient new drug development.
Possessing multi-stage production capabilities from small-scale trials to industrial manufacturing, supporting rapid sample supply and batch production to meet various R&D and production phase demands.

Conduct in-depth discussions with clients to thoroughly understand antibodies, payloads, and application environments; clarify technical specifications and development objectives. Combining industry experience, evaluate technical feasibility and potential challenges, formulate preliminary R&D plans and timelines to ensure smooth project initiation.
Based on β-galactosidase cleavage mechanisms and client requirements, design multiple linker structural schemes balancing enzymatic cleavage efficiency and in vivo stability. Use molecular modeling and chemical rationality analysis to select the optimal design, and communicate with clients for confirmation, ensuring scientific and reasonable design plans.
Develop efficient and reproducible synthetic processes, optimize reaction conditions to achieve high-purity linker synthesis. Prepare laboratory and pilot-scale samples to support client functional evaluation and application testing, laying the foundation for subsequent process scale-up.
Through in vitro enzymatic cleavage kinetics, plasma stability evaluation, and conjugation efficiency tests, comprehensively verify the linker's enzymatic specificity and stability. Ensure the linker maintains excellent function under various application conditions to meet client R&D needs.
Optimize synthesis processes based on laboratory procedures to realize pilot and industrial scale-up, ensuring product quality and batch-to-batch consistency. Establish strict quality control systems and standard operating procedures to guarantee efficient and stable linker production.

Provide detailed technical documentation and process reports to assist clients in technology transfer and production. Continuously track project progress, offer technical consultation and process optimization suggestions, ensuring comprehensive support throughout R&D and manufacturing.
β-Galactosidase is a hydrolase enzyme capable of recognizing and hydrolyzing β-galactosidic bonds, cleaving linkers to enable efficient drug release from carriers. Due to the elevated expression of β-galactosidase in tumor cells and certain pathological tissues, β-galactosidase-cleavable linkers have become an ideal design strategy for precise targeted drug delivery.
The core principle of β-galactosidase sensitive linkers lies in designing linkers containing β-galactosidase-sensitive structural units. When the ADC or drug carrier enters target cells or tissues, intracellular or extracellular β-galactosidase recognizes this structural unit and catalyzes hydrolysis, causing the linker to cleave and releasing the drug molecules for precise therapeutic effect. Enzymatic hydrolysis: β-galactosidase specifically recognizes the galactoside structure and cleaves the glycosidic bond. Targeted release: selective drug release occurs in the target cell environment, reducing systemic toxicity. Temporal and spatial control: enables controlled drug release in time and space, improving treatment efficacy and safety. This mechanism allows β-galactosidase sensitive linkers to effectively enhance drug selectivity and therapeutic index when designing antibody-drug conjugates.
High selectivity: β-galactosidase is overexpressed in specific cellular environments (e.g., tumor microenvironment), enabling precise drug release via enzymatic cleavage while sparing normal tissues. Good stability: linkers remain stable in blood circulation and are resistant to non-target enzyme cleavage, ensuring effective drug delivery to targets. Controlled drug release: enzymatic reactions regulate the drug release rate; linker design can be adjusted to tailor release kinetics for personalized therapy. Structural tunability: linker structures are flexible and can be chemically modified and optimized based on drug properties and target environment. Improved ADC efficacy: by reducing systemic side effects and increasing effective drug concentration within target cells, therapeutic outcomes are enhanced.
Beta-Galactosidase belongs to a class of hydrolytic lysosomal enzymes that degrade β-glycosidic linkages between galactose and its organic moieties. Kolodych et al. recently reported in vitro and in vivo activities of β-galactosidase-cleavable ADCs, demonstrating that galactosidase-based drug conjugates exhibited superior therapeutic efficacy in isolated mouse plasma compared to the approved trastuzumab emtansine for breast cancer treatment.
The design of β-galactosidase-cleavable linkers must be customized according to the specific antibody type, payload characteristics, and application environment of the ADC. BOC Sciences, with extensive design experience and professional expertise, provides one-stop custom development services for ADCs of various structures and functions, ensuring high compatibility between linkers, antibodies, and payloads. This achieves optimal conjugation efficiency and drug release performance, meeting diverse client R&D requirements.
Generally, the entire process from linker design and synthesis to provision of preliminary samples takes about 4 to 8 weeks. The exact duration depends on project complexity, difficulty of the required linker structure, and specific client needs. BOC Sciences adheres to a principle of efficient service, striving to shorten development cycles while ensuring quality and flexibly adjusting schedules to align with client R&D timelines.
BOC Sciences has a complete synthesis and production platform capable of meeting customer needs from research-grade small-batch samples to pilot and industrial-scale manufacturing. Whether for early-stage sample validation or subsequent commercial batch production, we provide stable process flows and strict quality controls to ensure product quality and batch consistency, fulfilling production demands at various stages.
We can provide β-galactosidase-cleavable linkers that comply with GMP standards according to client requirements. This includes GMP-grade raw material procurement, controlled production environments, comprehensive quality management systems, and documentation support, ensuring products meet regulatory requirements for drug development and clinical trials, thus facilitating smooth drug development and market approval.
Background
A leading biopharmaceutical company was developing a novel antibody-drug conjugate aimed at achieving precise drug release for specific tumor types. The main challenge faced by the research team was maintaining high plasma stability in vivo while ensuring efficient payload release triggered by β-Galactosidase within target cells. Existing commercial linkers could not meet the customized requirements, particularly regarding enzyme responsiveness, linker length, and payload stability.
How BOC Sciences Helped
BOC Sciences provided a full-process customized solution tailored to the client's needs, including:
Implementation Process
Key Results
Numerous scientific publications have employed linkers supplied by BOC Sciences, highlighting their essential contribution to ADC and bioconjugate design and development. Researchers have leveraged our high-quality linkers to successfully validate drug release mechanisms, assess cleavage efficiency, and conduct cell-targeting studies, with findings reported in internationally recognized journals.

"Their precise chemical design and careful optimization of linker-to-payload ratios ensured highly efficient enzymatic payload release in target cells while maintaining excellent plasma stability."
— Dr. Sophia Reinhardt, Senior Biochemist (Germany)
"They delivered robust, reproducible linkers specifically optimized for enzyme-triggered payload release in ADC constructs, providing detailed documentation and stringent quality control."
— Dr. Lucas Bennett, Lead Research Scientist (United Kingdom)
From cytotoxin synthesis to linker design, discover our specialized services that complement your ADC projects.
Find exactly what your project needs from our expanded range of ADCs, offering flexible options to fit your timelines and goals.
Contact our experts today for pricing and comprehensive details on our ADC offerings.










