An acid cleavable linker (acid labile linker) is a class of chemical linkers that can cleave under acidic conditions, commonly used in targeted drug delivery systems, especially antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). By leveraging the acidic pH characteristic of tumor tissues, intracellular lysosomes, or endosomes, such linkers enable controlled drug release in the targeted environment while remaining stable in the neutral pH environment of blood and normal tissues. Based on years of experience in chemical synthesis, conjugation chemistry, and ADC process development, BOC Sciences provides custom acid labile linker development services to global clients. Our services cover the full process from structural design, synthesis route optimization, to quality testing, ensuring product performance highly aligns with project requirements and facilitating efficient R&D and industrialization of next-generation ADC drugs.
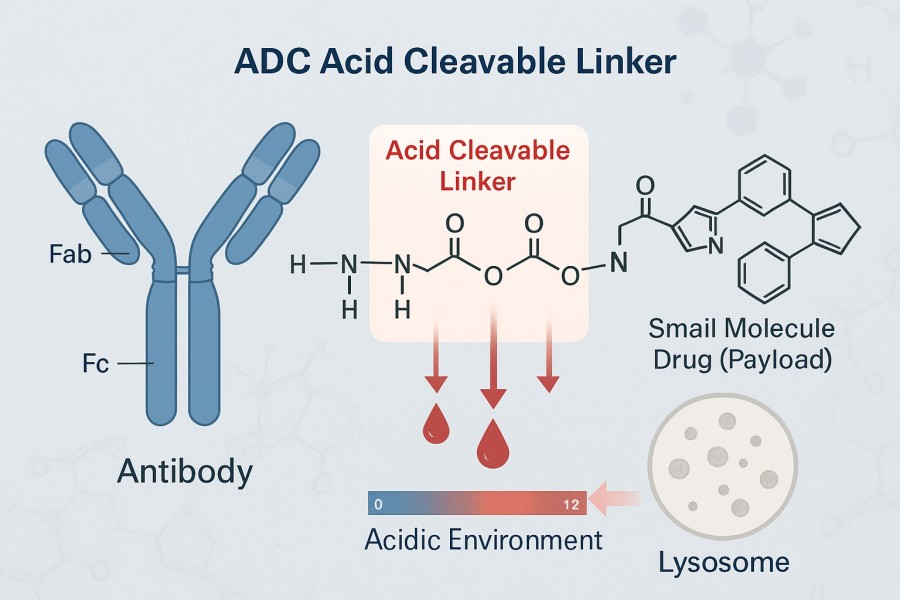
An acid labile linker is a special type of ADC linker containing chemical bonds sensitive to acidic conditions, such as hydrazone bonds, acetal bonds, ketals, and others. These bonds remain stable at normal physiological pH (~7.4) but rapidly cleave in acidic environments (such as lysosomes or endosomes of tumor cells, pH 4.5-6.5), thereby enabling precise payload release. The hydrazone linker is the most representative and widely applied acid labile linker. In the ADC field, acid labile hydrazone linkers are extensively used due to their high sensitivity to acidic environments, enabling precise drug release. Hydrazone linkers are stable at blood pH (~7.4) but rapidly cleave under the acidic pH (~4.5-5.5) inside tumor cells, achieving site-specific drug release.
BOC Sciences is committed to providing clients with comprehensive acid labile linker services from design, synthesis to optimization, with rich experience especially in custom development of acid labile hydrazone linkers. We flexibly adjust the cleavage rate and stability of pH-sensitive linkers according to different ADC project needs, ensuring precise and controlled drug release under physiological conditions. Our core service offerings include the following to support the rapid success of your ADC projects:
BOC Sciences specializes in customizing efficient multifunctional acid labile linkers. We tailor linker structures by selecting suitable acid-sensitive chemical bonds (such as hydrazone, acetal, ketal bonds) based on antibody properties, payload types, and release mechanism requirements to achieve precise and controlled drug release.
We provide structural modification services for acid labile linkers to regulate their acid sensitivity according to client-specific needs. For example, by introducing different substituents to modulate the electronic properties of hydrazone linker aldehydes, we precisely control the cleavage rate of pH-sensitive linkers to meet diverse ADC efficacy and safety requirements.
Using advanced organic synthesis and biochemical technologies, we develop efficient, scalable synthetic routes and optimize reaction conditions and purification processes to ensure linker stability under physiological conditions and efficient cleavage in acidic environments.
We support synthesis from laboratory scale to pilot and large-scale production to meet clients' needs at different stages. Our quality control system covers structural confirmation, purity testing, and functional assays to guarantee stable and reliable product performance.
In ADC R&D, linker design must balance the antibody's structural characteristics and the chemical nature of the payload to achieve optimal drug delivery. BOC Sciences deeply understands the complex interactions between antibodies and drug molecules, offering tailor-made acid labile linker design services to ensure linkers maintain stable circulation in vivo while efficiently cleaving to release drugs under tumor microenvironment or intracellular acidic conditions.
In ADC design, the chemical and physical properties of the payload are critical factors influencing linker selection. BOC Sciences provides customized acid labile linker solutions based on payload molecular structure, solubility, chemical stability, and mechanism of action.
Key Services:
BOC Sciences recognizes that different antibody molecular structures directly affect linker selection and conjugation efficiency. When designing acid labile linkers, we deeply analyze antibody amino acid composition, spatial conformation, and modifiable sites to ensure efficient, stable, and controllable binding with antibodies.
Key Services:
Possessing extensive experience in the development of various ADC linkers including acid cleavable, enzyme cleavable, and reduction-sensitive linkers, we provide optimal design and manufacturing solutions tailored to different targets and payloads.
Through precise chemical modifications and functional group introduction, we ensure acid cleavable linkers remain stable in blood circulation yet efficiently cleave in acidic environments, achieving effective drug release.
Offering full-process scale-up capabilities from laboratory to industrial production, we optimize reaction and purification procedures to guarantee batch consistency and high purity of acid cleavable linkers.
Manufactured in compliance with ISO and cGMP standards, equipped with analytical platforms including HPLC, LC-MS, NMR, and IR, we comprehensively test linker structure, purity, and stability.
Based on antibody characteristics, payload physicochemical properties, and therapeutic requirements, we tailor the design and process of acid cleavable linkers to meet diverse ADC development needs.
Providing full-cycle support from feasibility assessment to process optimization, clients can choose flexible collaboration modes including custom R&D, joint development, or contract manufacturing.

Deep communication with clients regarding antibody properties, payload types, and pharmacological goals to assess acid labile linker compatibility and develop preliminary R&D direction and technical routes.
Selecting acid-sensitive chemical bonds such as hydrazone, acetal, ketal according to release mechanism and stability requirements, designing linkers that balance stability in blood and rapid cleavage in acidic conditions.
Establishing efficient, scalable chemical synthesis processes, optimizing reaction conditions and purification methods to ensure linker purity, yield, and batch consistency.
Adjusting conjugation conditions between antibody, linker, and payload to control DAR value, improve conjugation efficiency and stability, achieving optimal drug release performance and safety.
Employing HPLC, LC-MS, NMR, and other technologies for comprehensive assessment of structure, purity, stability, and acid cleavage rate, ensuring linkers meet ADC development standards.

Providing complete technical data packages, process transfer, and production guidance; continuously optimizing linker performance based on project feedback to support scale-up and commercialization.
Acid-cleavable linkers are stable in alkaline environments but highly sensitive to acidic environments, such as hydrazone linkers. Acid-cleavable linkers exploit the low pH within endosomes and lysosomes to trigger hydrolysis of the acid-labile hydrazone linker, subsequently releasing the payload. These linkers have been linked to non-specific drug release in clinical studies. A prime example is BR96-doxorubicin (BR96-Dox), constructed by conjugating doxorubicin to the monoclonal antibody BR96 via an acid-cleavable hydrazone. After binding to target tumor cells, BR96-Dox is internalized by endocytosis into lysosomes. Clinical trials have shown BR96-Dox is not associated with the typical side effects of native doxorubicin and can potentially deliver high doses of doxorubicin to antigen-expressing tumors, enabling complete remission and cure of subcutaneous human breast, lung, and colon tumors.
Hydrazone linkers exhibit pH-dependent stability: stable at neutral pH (bloodstream) and hydrolyzed in acidic media (pH < 6 for endosomes and pH < 5 for lysosomes) to form corresponding ketone and hydrazine. This approach has been successfully applied in IMMU-110, which contains a cleavable acyl hydrazone linker formed by reaction between the hydrazide of 4-maleimidomethyl cyclohexane-1-carboxylate (MCC) and the keto group of doxorubicin. Hydrazone linkers are also frequently associated with calicheamicin payloads. In this context, release involves a two-step activation: first, acid-sensitive hydrazone hydrolysis; second, disulfide bond reduction by glutathione (GSH), allowing cyclization of the sulfhydryl intermediate. During development, the stability of various hydrazones was tested at pH 4.5 and pH 7.4. Hydrazone linkers stable at pH 7.4 and labile at pH 4.5 yielded the most potent and effective ADCs in vitro and in vivo in mice.
An acid-labile group is a chemical functional group that remains stable under neutral or alkaline conditions but cleaves or undergoes structural changes under acidic conditions. In ADCs, acid-labile groups leverage the acidic microenvironment of tumor cells or intracellular lysosomes to achieve precise drug release, enhancing targeting and reducing systemic toxicity.
Hydrazone linkers are commonly used acid-labile linkers that conjugate antibodies to drugs via hydrazone bonds. These bonds remain stable at physiological pH (~7.4) but rapidly hydrolyze and cleave under acidic conditions (pH 4.5–6.5). This mechanism allows the hydrazone linker to remain stable in the bloodstream but release active drugs in the acidic environment of tumor cells, enabling precise cytotoxic effects.
BOC Sciences designs acid labile linker structures tailored to the antibody type, payload physicochemical properties, and therapeutic requirements provided by the client. By optimizing the selection of acid-sensitive bonds and molecular design, combined with efficient synthesis and purification processes, we ensure the linker is stable under physiological conditions and efficiently cleaves under acidic environments. We also provide conjugation condition optimization and quality testing to guarantee the custom linker meets specific project requirements.
To ensure stability of acid labile linkers under physiological conditions, BOC Sciences employs precise chemical modifications and strict process control to optimize linker structure, making it resistant to cleavage in blood. Meanwhile, the design ensures rapid hydrolysis in acidic environments (such as intracellular lysosomes in tumor cells) for effective payload release. Multiple analytical methods are applied to verify product stability and batch-to-batch consistency.
Acid labile linkers are compatible with a wide range of payloads, including small molecule cytotoxins (e.g., DM1, MMAE), radioactive labels, and nucleic acid drugs. Their acid-sensitive cleavage enables precise payload release in the acidic environment of tumor cells, improving therapeutic efficacy while accommodating the diverse physicochemical properties of different payloads to meet varied ADC development needs.
Background
A biopharmaceutical company was developing an antibody-drug conjugate targeting solid tumors, aiming to achieve tumor microenvironment-specific payload release. However, the R&D team faced two major challenges: first, existing linkers exhibited insufficient plasma stability, leading to premature non-specific drug release; second, the payload release efficiency in the acidic tumor microenvironment was suboptimal. To ensure both efficacy and safety of the ADC, the team required a customized hydrazone-type acid-labile linker to precisely control drug release.
How BOC Sciences Helped
BOC Sciences provided a fully customized, end-to-end solution:
Implementation Process
Key Results
BOC Sciences possesses extensive research and application experience in the field of ADC linkers. Its high-quality linker products and solutions have been widely cited in internationally renowned journals and scientific publications. These studies have not only advanced the development of ADCs and other bioconjugation technologies but also provided reliable technical and data support for global researchers in the design of next-generation targeted drugs.

"Their proficiency in hydrazone chemistry ensured excellent plasma stability and precise payload release under acidic tumor conditions. Clear communication and timely updates significantly accelerated our ADC development process."
— Dr. Isabella Moreno, Senior Medicinal Chemist (Spain)
"The team at BOC Sciences demonstrated outstanding technical capability in designing and synthesizing our acid-sensitive linkers. Their iterative optimization and rigorous analytical validation ensured consistent performance and reproducibility."
— Dr. Hiroshi Tanaka, Principal Scientist, Drug Delivery (Japan)
"Working with BOC Sciences on custom hydrazone linkers was seamless. They expertly balanced linker stability and trigger responsiveness, providing comprehensive documentation and quality control that aligned perfectly with our internal standards."
— Dr. Eleanor Scott, ADC Research Scientist (United Kingdom)
"Their deep understanding of chemical design, combined with thorough functional testing, enabled reliable payload release in tumor-like acidic environments. Professionalism and responsiveness throughout the project were outstanding."
— Dr. Markus Vogel, Senior Biochemist (Germany)
From cytotoxin synthesis to linker design, discover our specialized services that complement your ADC projects.
Find exactly what your project needs from our expanded range of ADCs, offering flexible options to fit your timelines and goals.
Contact our experts today for pricing and comprehensive details on our ADC offerings.










