Enzymatic conjugation is an advanced bioconjugation technology that uses specific enzymes to catalyze reactions and achieve highly controlled conjugation at predefined antibody sites. In the development and commercialization of antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), enzymatic conjugation is gradually replacing traditional random chemical methods, becoming a key approach for constructing ADCs with high homogeneity, stability, and predictable in vivo behavior. As a technology-driven company focused on ADC products and services, BOC Sciences leverages a mature enzyme engineering platform and antibody modification expertise to provide clients with full-process enzymatic conjugation solutions, covering critical steps from feasibility assessment and antibody engineering design to process scale-up and quality analysis.
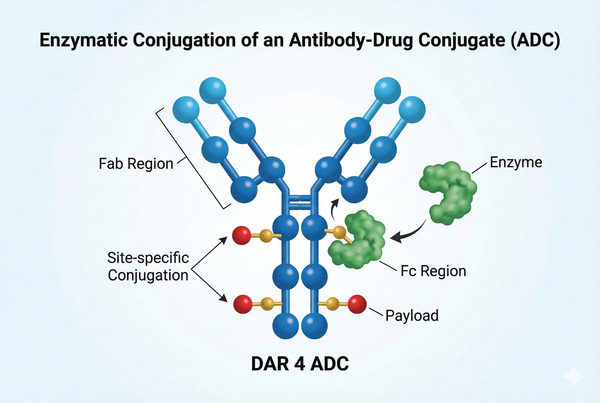
The therapeutic index, safety, and clinical success of ADCs largely depend on the conjugation strategy. Random lysine or cysteine conjugation often results in wide drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) distributions and high structural heterogeneity, impacting pharmacokinetics and increasing toxicity risk. In contrast, enzymatic conjugation enables site-specific modification and precise DAR control, significantly improving ADC critical quality attributes (CQA) and emerging as a core technology for next-generation ADC design. This method uses enzymes that recognize specific amino acid tags to achieve site-specific antibody conjugation. Additionally, by inserting specific amino acid tags into the antibody sequence, payloads can be selectively attached. These tags are recognized by specific enzymes, such as formylglycine generating enzyme (FGE), microbial transglutaminase (MTG), sortase, or tyrosinase, enabling precise site-specific conjugation.
BOC Sciences' enzymatic conjugation services focus on ADC development, following the design principle of "precision, controllability, and scalability" to provide high-quality conjugation solutions for innovative ADCs and various bioconjugates. Through a mature enzymatic conjugation technology platform, we can design defined and highly reproducible antibody conjugation sites, precisely control DAR with narrow distribution, and preserve both antigen-binding activity and Fc function, meeting the strict requirements for structural homogeneity and quality consistency in preclinical studies and IND submissions.
Transglutaminase is one of the most established enzymatic conjugation tools in the ADC field. It catalyzes the formation of stable covalent amide bonds between specific glutamine residues and primary amine linkers or drug molecules. BOC Sciences can assist clients in glutamine site selection, antibody sequence optimization, and scale-up of conjugation conditions.
The antibody Fc region naturally contains N-linked glycans, making it an ideal site for site-specific modification. By combining glycosidases and glycosyltransferases, functional groups can be introduced at the Fc glycan termini for precise conjugation. This strategy is particularly suitable for ADC projects requiring stringent PK/PD behavior.
Sortase A is a transpeptidase recognizing short peptide motifs (e.g., LPXTG), allowing highly controlled modular conjugation at the antibody C-terminus or Fc region. BOC Sciences provides one-stop technical support from tag design to conjugation validation.
FGE catalyzes the conversion of specific cysteine residues to formylglycine (fGly), introducing unique and highly reactive aldehyde functional groups on the antibody. BOC Sciences offers full technical support from antibody sequence engineering and FGE modification to payload conjugation and structural characterization.
BOC Sciences employs multiple enzymatic conjugation strategies to achieve precise modification at predefined antibody sites, avoiding the structural heterogeneity of traditional random conjugation and ensuring consistent ADC configurations for reliable efficacy and safety studies.
By systematically optimizing enzyme reaction parameters and engineered antibody sites, we achieve accurate DAR control with narrow distribution, significantly improving therapeutic index, reducing toxicity risk, and meeting high-quality candidate screening requirements.
BOC Sciences selects stable enzymatic covalent linkages to reduce in vivo payload detachment and ensures ADC stability during storage and in physiological conditions through systematic structural characterization.
Site-specific and structurally homogeneous ADCs provide more predictable pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Our enzymatic conjugation strategies minimize clearance variability, supporting smooth transition of ADC projects into clinical development.
With mature platforms including Transglutaminase, Glycoengineering, Sortase A, and FGE, BOC Sciences has comprehensive laboratory and analytical capabilities to flexibly meet diverse ADC architectures and technical requirements.
We provide end-to-end services from conjugation design, process development, to quality analysis, while supporting highly customized solutions and long-term technical collaboration. Continuous communication and professional support enable efficient advancement of ADC projects.

Based on antibody structure, target information, payload type, and desired DAR, we comprehensively evaluate ADC design requirements, select the most suitable enzymatic conjugation strategy, and establish a feasible, scalable technical route.
For site-specific conjugation, we perform antibody sequence analysis and engineering design, including Fc modification, specific enzyme recognition sites, or peptide tag insertion, while assessing structural stability and functional impact.
For the selected enzymatic system, we optimize enzyme amount, reaction time, temperature, pH, and substrate ratio to improve conjugation efficiency, control side reactions, and ensure structural homogeneity and reproducibility of ADCs.
We use multiple purification strategies to remove unconjugated components and free payload, and systematically analyze DAR distribution, molecular integrity, and aggregation levels using LC–MS, HIC, SEC-HPLC, and other methods.
Based on lab optimization, we support ADC preparation from milligram to gram scale, and verify conjugation efficiency, DAR distribution, and structural consistency across batches to meet preclinical research requirements.

We provide complete process parameters, analytical data, and technical reports, and continue offering optimization advice and technical support throughout the project, facilitating efficient advancement of ADC development.
Enzymatic conjugation is a technique that uses specific enzymes to achieve site-specific conjugation at predefined antibody locations. Compared to traditional random chemical conjugation, this approach significantly reduces structural heterogeneity, enables precise DAR control, and helps improve ADC stability, safety, and clinical predictability.
Lysine and cysteine conjugations are typically random modifications, often resulting in wide DAR distributions and high batch-to-batch variability. Enzymatic conjugation, in contrast, relies on the high specificity of enzymes to react at fixed positions, producing structurally homogeneous, high-quality ADC configurations.
With rational site selection and optimized reaction conditions, enzymatic conjugation can typically achieve mainstream designs such as DAR 2 or DAR 4 while maintaining narrow distributions. BOC Sciences can assist in developing the optimal DAR strategy based on payload characteristics and project requirements.
Properly designed enzymatic conjugation is usually positioned in the Fc region or away from the antigen-binding site, avoiding interference with antibody recognition. Through systematic engineering and functional evaluation, BOC Sciences maximizes the retention of antibody activity and Fc-mediated functions.
We support multiple mainstream ADC enzymatic conjugation technologies, including Transglutaminase, Fc glycoengineering, Sortase A, and FGE-mediated strategies, providing flexibility to accommodate different antibody structures and linker–payload systems.
Yes. We offer comprehensive ADC structural and quality characterization services, including DAR distribution, purity, aggregation, and stability analysis, ensuring that enzymatically conjugated ADCs meet critical quality attribute requirements for R&D and regulatory submissions.
Background
A U.S. biopharmaceutical company was developing an ADC targeting solid tumors, aiming to construct a DAR 4, highly homogeneous ADC for preclinical animal studies. Traditional lysine conjugation led to heterogeneous ADCs, wide drug-load distributions, and partial loss of antibody binding activity, affecting pharmacokinetics (PK). The client sought site-specific conjugation to improve ADC quality and predictability while maintaining scalable production.
How BOC Sciences Helped
BOC Sciences analyzed the client's antibody structure and payload properties and recommended a Transglutaminase (TGase)-mediated enzymatic conjugation strategy. Our team provided full-process technical support, including:
This approach enabled the client to achieve highly homogeneous conjugation while preserving antibody antigen-binding activity and Fc functions.
Implementation
Results
Browse BOC Sciences' publications to explore articles from research teams worldwide, showcasing the scientific contributions of our products and services in cutting-edge drug development.

"BOC Sciences helped us optimize a site-specific ADC using Transglutaminase conjugation. Their team provided clear guidance, rapid prototyping, and consistent quality across multiple batches. We could confidently advance our preclinical studies thanks to their expertise."
— Dr. James Carter, Senior Scientist (USA)
"Working on a complex ADC project with tight preclinical timelines, BOC Sciences provided precise enzymatic conjugation and detailed analytical support. The uniformity and stability of the ADCs exceeded our expectations. They are a reliable and knowledgeable partner."
— Prof. Emily Thompson, ADC Development Lead (UK)
"BOC Sciences' enzymatic conjugation service allowed us to achieve controlled DAR and maintain antibody functionality. The technical team was highly responsive and guided us through process optimization efficiently. Their professionalism makes them stand out in the field."
— Dr. Michael Bauer, Biologics Research Scientist (Germany)
"We faced challenges scaling site-specific ADCs for in vivo studies. BOC Sciences delivered high-quality enzymatic conjugation solutions with reproducible results and comprehensive documentation. Their support significantly accelerated our project timeline."
— Ms. Laura Davis, Preclinical Development Manager (France)
From cytotoxin synthesis to linker design, discover our specialized services that complement your ADC projects.
Find exactly what your project needs from our expanded range of ADCs, offering flexible options to fit your timelines and goals.
Contact our experts today for pricing and comprehensive details on our ADC offerings.










